Welcome Clients!
Sign up for Warhead Free Newsletter and receive eCommerce tips, strategies, best practices and info on Warhead updates.
Sign up Today!
Terminology
URL Slug: Is the exact address of a specific page on a website. It is what comes after the domain name and the .com. For example, for the URL www.kreativesports.com/footwear, the /footwear is the URL slug for that page.
Page Title: Also known as title tags, the page title is an element used to define the title of a page on a website. The page title is intended to be used as a short description of that page’s content and is commonly used on search engine result pages (SERPs) to preview snippets for a given page.
Meta Description: Meta descriptions provide concise explanations of the content on a web page and are often used on search engine result pages (SERPs) to display preview snippets for a given webpage.
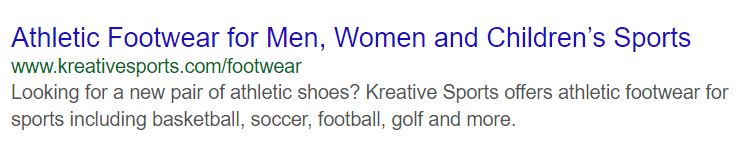
SERP: A search engine results page (SERP) is the webpage displayed by a search engine as a result of a search query done by a user searching the web. The search engine results page will display several website listings as a result of the user’s keyword or search query. Below is an example of an individual search engine result that you would see on a search engine results page.
|
|
|
|
Search Engine: A piece of software program that searches for and identifies items in a database that correspond to keywords or characters specified by the user, used especially for finding particular sites on the World Wide Web.
Search Query: A query is essentially a keyword or keyword phrase that a user enters into a search engine in an effort to find a website that provides the information they are looking for.
Targeted Keyword: Is the primary keyword that you’re trying to target for a given page on your website. When you tie these terms into your page titles, meta descriptions and on page content, you are telling the search engines that these words have more importance and relevancy (see definition below), so this should be the keyword that best describes a page on your website. NOTE: It is important to keep in mind the level of competition when selecting a targeted keyword. You don’t want to assume what that keyword will be; you will need to do some research in order to identify what that keyword is.
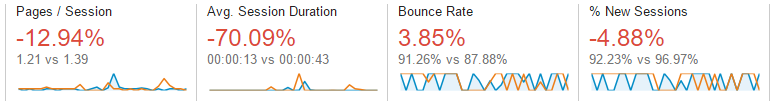
Search Relevancy: If your website is ranking under a particular keyword term or search query, a user that visits the site from a search engine results page will be likely to stay on and navigate through the website because it is relevant to what they searched for. If your site was not relevant to the users search query, they are likely to click the back button and exit the site fairly quickly. This can lead to negative statistics such as lower pages per visit, less time on the site and a higher bounce rate (see definition below) for the site. These statistics, like what you see in the screenshot below can be found in your Google Analytics account.
Search engine spiders (crawler /bots): A spider is a program that visits websites and reads their pages and other information in order to create entries for a search engine index. The major search engines on the Web all have such a program and they are often times referred to as a "crawler" or a "bot."
Index: Search engine spiders crawl through pages of websites to examine the contents of those pages. Once the content has been examined and the search engine has an understanding of what that page is about, that page will be ‘indexed’ so that it shows up in that search engines results pages.
On Page Content: Content that is displayed on the site that a visitor can read. This content is intended to describe what that particular page is about on the website. Search engines will also look to see if the content on the page is consistent with the page title and meta description for the page. Having optimized on page content for each category, product and brand page is highly recommended.
Google Analytics: Is a web analytics service offered by Google that tracks and reports website traffic. Once your website has been set live, this is an extremely valuable tool that can be used to help you identify the pages on the site that would be the most beneficial for you to optimize. To learn more about Google Analytics and how you can utilize the information in your analytics account to improve the performance of your website, you can take some free online courses through the Google Analytics Academy by going to the following link: https://analyticsacademy.withgoogle.com
Bounce rate: Is an analytics term and represents the percentage of users who visit the site and exit it from the same page they landed on. They essentially click the back button before going on to view a second page on the site. You want your bounce rate to be low. This usually occurs when the users are not finding anything on that page of the site that is relevant to what they were looking for.
Google Search Console: Formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, Google Search console allows webmasters to check indexing status and optimize visibility of their websites to help you monitor and maintain your site's presence in Google search results. Among other things, this tool will help you understand how Google views your website and can be used to help you identify which pages might be most beneficial for you to optimize in order to position yourself better in search results. To learn more about Google Search Console and how you can use the information it offers to improve your site, you can go to the following link: https://support.google.com/webmasters/.
Bing Webmaster Tools: Allows webmasters to check indexing status and optimize visibility of their websites to help you monitor and maintain your site's presence in Bing search results. Among other things, this tool will help you understand how Bing views your website and can be used to help you identify which pages might be most beneficial for you to optimize in order to position yourself better in search results. For more information on Bing Webmaster Tools, here is a link to their Help & How-To Center: https://www.bing.com/webmaster/help/
Google AdWords: AdWords (Google AdWords) is an advertising service by Google for businesses wanting to display ads on Google and its advertising network. The AdWords program enables businesses to set a budget for advertising and only pay when people click the ads. The ad service is largely focused on keywords.
Google AdWords Keyword Planner Tool: Within Google AdWords is the ‘keyword planner tool’. This tool can be used to conduct keyword research. The keyword planner helps find the top keywords that describe the product or service online businesses have to offer based on ‘average monthly search volume’ and the ‘level of competition’.
Average monthly search volume: The average number of times people have searched for the exact keyword based on the location and Search Network targeting that you've selected. By default, the number of searches for the keyword is averaged over a period of 12 months.
Competition: The number of advertisers that showed on each keyword relative to all keywords across Google. Note that this data is specific to the location and Search Network targeting that you've selected. When you’ve done a search using the keyword planner tool, you can see whether the competition for a keyword is low, medium, or high.
Long tail keywords: Are those three to five keyword phrases which are very, very specific to the product or service you’re offering. Typically, when an online shopper uses such a specific keyword phrase, they know exactly what they’re looking for with the intent of buying or obtaining that product or service. This means that websites found based on a customer who searchers for a longer tail keyword have a higher likelihood of converting. For example, a person searching for ‘shoes’ is probably just browsing the internet for information, but not necessarily looking to buy. Whereas someone searching for ‘Nike Hyperdunk 2015 Mens Basketball Shoe Size 10’ practically has their wallet out and are ready to buy.
With long tail keywords search engines such as Google are sophisticated enough to read multiple variations of keywords. For example, say you take the keyword ‘Mens Hightop Basketball Shoes’. Search engines can read different variations of that keyword such as:
- Mens Hightop Basketball Shoes
- Mens Basketball Shoes
- Hightop Basketball Shoes
- Basketball Shoes
- Shoes